How Do You Choose the Right Ejection System for Your Mold?
Industrial Components
Large or heavy parts, like machinery housings, often require hydraulic ejection for sufficient force and control.
Air ejection is exclusively used in the medical industry.False
While common in medical applications, air ejection is also used in other industries for delicate or thin-walled parts.
Hydraulic ejection is necessary for large industrial parts.True
Hydraulic systems provide the power needed to eject large, heavy parts without damage.
What Are the Differences Between Mechanical and Non-Mechanical Ejection Systems?
Ejection systems can be categorized into mechanical and non-mechanical types, each with distinct advantages and applications.
Mechanical systems (pins, blades) use physical force, while non-mechanical systems (air, hydraulic) use pressure or fluid power, offering different benefits based on part needs.
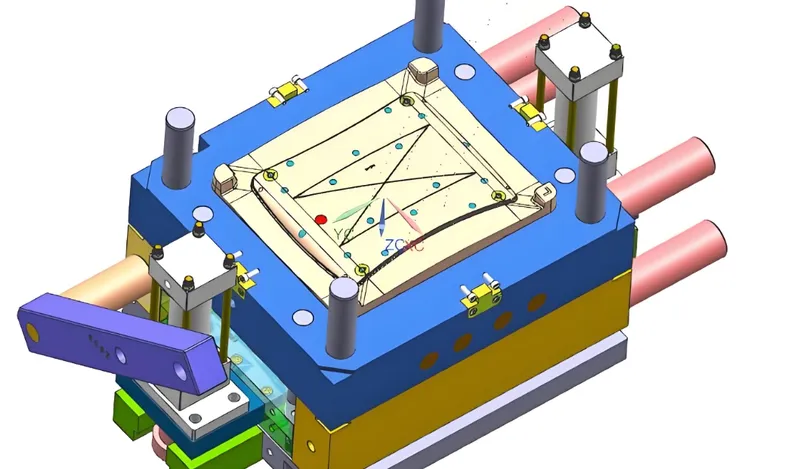
Mechanical Ejection
- Examples: Pins, blades, sleeves, strippers.
- Advantages: Simple, cost-effective, easy to maintain.
- Disadvantages: Can leave marks, may not suit delicate parts.
Non-Mechanical Ejection
- Examples: Air ejection, hydraulic ejection.
- Advantages: Gentle on parts, suitable for complex or large components.
- Disadvantages: Higher cost, more complex setup.
Mechanical ejection systems are always preferable due to their simplicity.False
While simple, mechanical systems may not be suitable for all parts, especially delicate or complex ones.
Non-mechanical systems are more versatile for various part types.True
Systems like air or hydraulic ejection can handle a wider range of part geometries and materials.
How Do You Design an Effective Ejection System?
Designing an effective ejection system requires careful consideration of part and mold characteristics to ensure smooth operation and part quality.
An effective ejection system balances force distribution, minimizes part damage, and accommodates material properties, with key design elements like draft angles and ejector placement.
You may also interested in: